Give $20, Get $20 — Refer a friend and get $20 off your next order! Learn More >
CBDA & CBD: What’s The Difference?

You may already be familiar with CBD, or cannabidiol, the non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in the hemp plant. Unlike THC, CBD won’t get you high, but its positive effects have long been touted by users, from chilling you out to amping up your libido. But there is much more to Cannabis and hemp than CBD and THC. Other potent compounds exist in the plant, including CBDA, or cannabidiolic acid. While closely related to CBD, CBDA has its own unique function. Learn what this function is, as well as the crucial differences between CBD vs. CBDA.
CBDA Begins as CBGA
It’s impossible to talk about CBDA without first mentioning CBGA, or cannabigerolic acid. Sometimes referred to as the “mother of all cannabinoids” or the “mothership,” CBGA is the origin of all cannabinoids. It interacts with plant enzymes to convert to three major cannabinoid precursor compounds: THCA, CBCA, and CBDA. When the Cannabis plant is exposed to sunlight or heat after such interaction, decarboxylation occurs to remove the carboxyl group and CBDA converts to CBD. This decarboxylation process can happen in an instant, such as when vaporizing, smoking, or cooking, but it can also happen gradually when the raw plant matter is left to sit at room temperature.
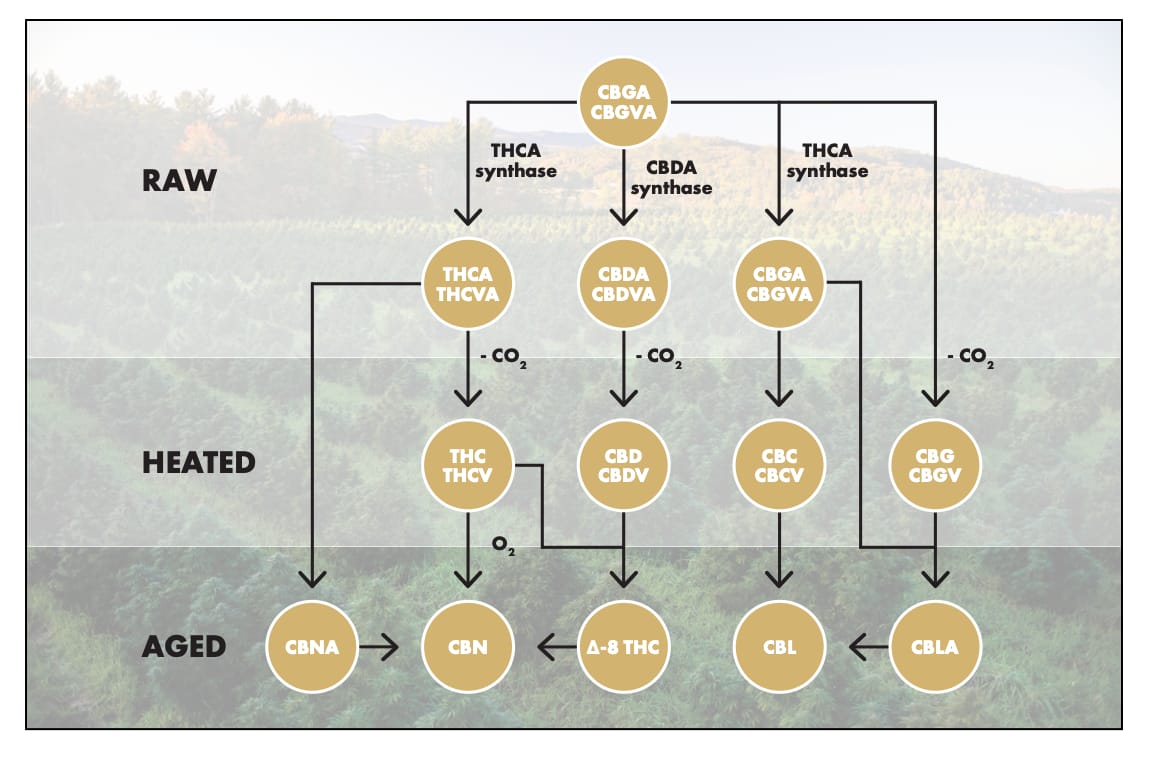
CBDA vs. CBD
An estimated 113 cannabinoids can be found in hemp, with CBDA and CBD being just two of them. Both CBDA and CBD are non-psychotropic cannabinoids, so they will not produce that euphoric sensation attributed to THC. While CBDA’s traits are similar to those found in CBD, CBDA has been shown to have greater bioavailability than CBD, meaning the body can absorb more of it.
The easiest way to think about CBDA is as the precursor or rawest form of CBD. Most cannabinoids bind directly with either the CB1 or CB2 receptors, but CBDA works in an entirely different way. It interacts with the endocannabinoid system by inhibiting the COX-2 enzyme.
How to Take CBDA
Some people juice raw and uncured Cannabis to benefit from CBDA, but products are available that use raw hemp or offer a broad array of cannabinoids like CBDA, along with terpenes and flavonoids that occur naturally in the plant. These more-comprehensive products are often referred to as “full-spectrum,” and may come as a capsule, tincture, or topical.
Full-spectrum CBD products with CBDA contribute to the entourage effect, which refers to the natural interaction of these botanicals when consumed together. While CBD alone has its benefits, the synergy of the compounds hold more potential when blended to create a more harmonious experience in the user.
CBDA may not be as well known as CBD, but it is a crucial component to the hemp plant because without it, CBD wouldn’t exist.
To explore a variety of full-spectrum CBD products, visit Upstate Elevator Supply Co.
Erica Garza is an author and essayist. Her work has appeared in TIME, Health, Glamour, Good Housekeeping, Women’s Health, the Telegraph, and VICE. She lives in Los Angeles.




